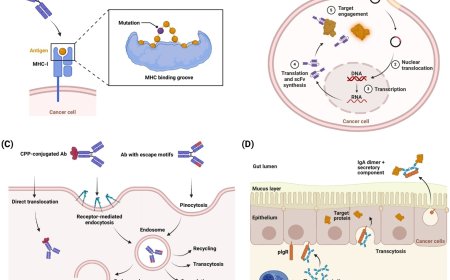
How exercise may control diabetes via gut microbiome-adipose crosstalk
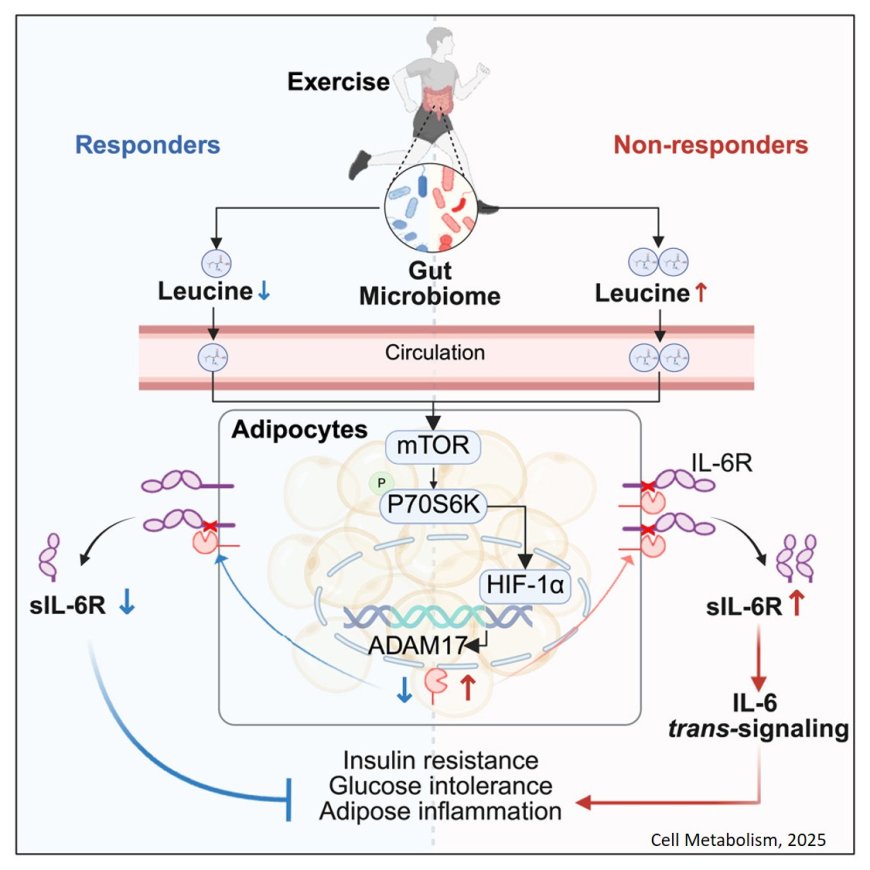
There is a wide interpersonal variability in prevention and management of diabetes via exercise.
The researchers identify soluble interleukin-6 receptor (sIL-6R) as a key exerkine determining the efficacy of exercise in diabetes prevention.
Mechanistically, the authors show that elevated gut microbiome-mediated leucine in non-responders acts on white adipocytes to promote disintegrin and metalloproteinase 17 (ADAM17)-mediated sIL-6R production via the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)-hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF1α) pathway.
This in turn impairs the metabolic benefits of exercise through interleukin (IL)-6 trans-signaling-induced adipose inflammation. which is modulated by microbiome-dependent leucine through a gut-adipose tissue axis.
Pharmacological or dietary interventions targeting adipocyte-secreted sIL-6R may help to improve the metabolic outcomes in those exercise non-responders.
https://www.cell.com/cell-metabolism/fulltext/S1550-4131(25)00473-5